
Features
3 MIN READ

Lack of pigmentation makes the turtle appear golden in colour
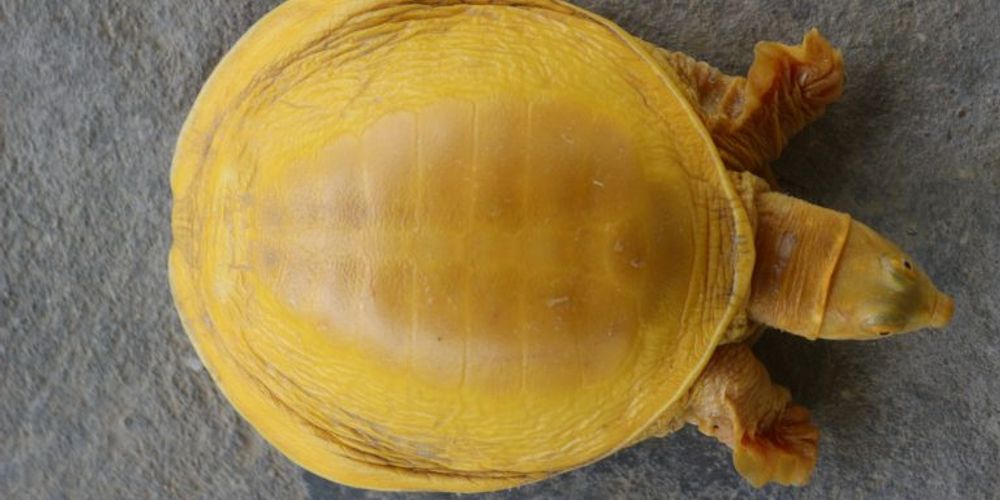

After news of the existence of a yellow turtle in India's eastern state of Odisha went viral this past July, Nepalis wanted to remind the world that they made a similar discovery first — on April 14, 2018, to be exact — when a rare, golden turtle — but a different species — was found for the first time in southeastern Nepal’s Dhanushadham municipality.
According to a research paper by Kamal Devkota, Dev Narayan Mandal and Hinrich Kaiser, which was published in the journal Herpetology Notes, the turtle was released into its natural habitat after pictures were taken as proof.
In an email interview with Global Voices, Devkota explained:
Our team member, Chandradeep Sada, rescued this rare golden turtle from Dhanushadham Municipality, Nepal on April 14, 2018. Later, Dev Narayan Mandal identified it as an Indian flapshell turtle [scientific name Lissemys punctata]. We further researched it and found that the colour aberrations are quite rare in nature. The lack of body pigmentation made the turtle appear golden coloured, with only the eyes showing a dark pigmentation.
This is the first chromatic leucism in L. punctata in Nepal, which is the first for the northern subspecies of L. punctata and the fifth documented observation in the species. That's why it is very important for conservationists and researchers.

A normal Indian flapshell turtle is greenish-grey in colour, with yellow marks on its head and neck. It has a grey carapace dotted with dark yellow spots and derives its name from the femoral flaps at the plastron, the ventral part of the shell.
These turtles are found in Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka, most typically in ditches, lakes, ponds and paddy fields with stagnant water. Omnivorous in nature, they eat anything from leaves and flowers to snails, fish and frogs.
While a normal-coloured flapshell turtle can easily camouflage itself in the murky, greenish water, its golden-coloured variant — a turtle with chromatic leucism — is easily recognisable and therefore more vulnerable. Its luminous golden colour, in particular, makes it a prized pet.
The congenital disorder of albinism creates a complete absence of pigmentation in the skin, hair and eyes due to the lack of tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in the production of melanin. Researchers estimate that albinism occurs once in every 10,000 mammal births.
Leucism, on the other hand, is an extremely rare genetic condition in which animals have reduced pigmentation. Most leucistic animals have normal-coloured eyes, whereas those with albinism tend to have red or pink eyes.
Nepal is home to 16 species of turtles, of which four are critically endangered: the three-striped roofed turtle (Kachuga dhongoka), the red-crowned roofed turtle (Kachuga kachuga), the Indian narrow-headed softshell turtle (Chitra indica) and the elongated tortoise (Indotestudo elongate).
Though turtles play an important role in reducing pollution by feeding on insects, vegetation and dead animals, factors like habitat loss, fragmentation and degradation have been threatening their survival.
According to “Turtles of Nepal – A Field Guide for Species Accounts and Distribution,” the draining of wetlands for irrigation and fishing, the excessive use of agrochemicals which eventually seep into waterways and unsustainable fishing methods all negatively impact turtle populations.
Adding to their woes is the illegal trade for keeping turtles as pets, as well as their use in traditional medicine. Some people believe in eating turtles and their eggs to achieve improved health, longevity and virility. Turtle shells are also used to make curio items.
Despite such threats to Nepal’s turtles, conservationists and other local bodies, such as the Turtle Rescue and Conservation Center in eastern Nepal, have been working to save these magnificent creatures.
This article was previously published in Global Voices, an international and multilingual community of writers, translators, academics, and human rights activists.
::::::
Features
8 min read
How apologists for untouchability are using the pandemic’s social-distancing rules as proof that societal notions of purity have merit
COVID19
News
5 min read
The government’s recent stringent measures seem to be a response to more and more public figures getting infected
COVID19
News
3 min read
A daily summary of Covid19-related developments that matter
Perspectives
7 min read
The communities living near Nepal’s protected areas live in constant fear of wild animals and the security forces
COVID19
News
4 min read
A daily summary of Covid19 related developments that matter
Books
3 min read
The goal is to get your attention, then show you advertisements.
Features
5 min read
Kathmandu air pollution will have long-term impacts not just on public health but also on individual cognition and the national economy.
Photo Essays
4 min read
The lockdown has made it exceedingly difficult for Tul Bahadur Baram to get the dialysis treatment he needs