
Features
5 MIN READ

Research paper led by a Nepali author explains the rare phenomenon of 'leucism' in two krait species
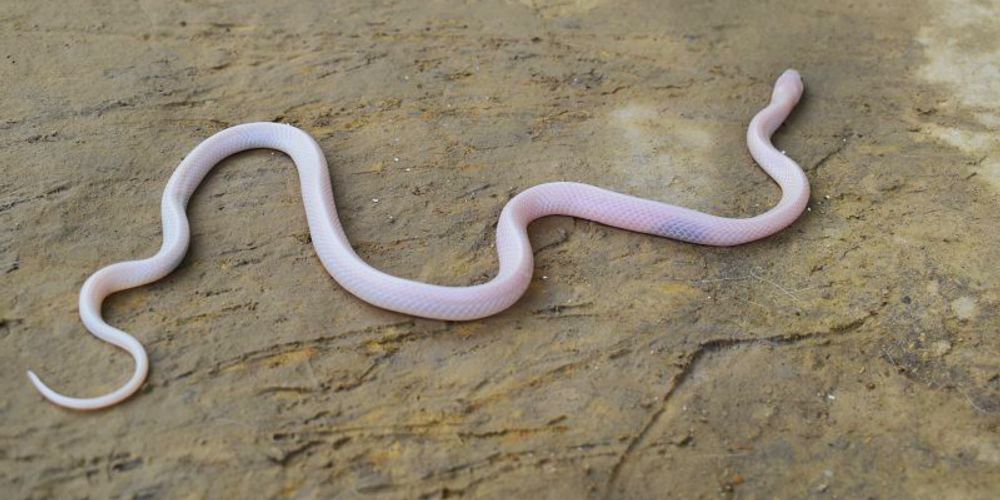

According to a research paper published in October 2020, two white-coloured kraits (of the genus Bungarus) discovered during rescue calls in Nepal's southeastern region of Province No. 2, are the first such recorded cases in their species. Kraits are known to be some of the most venomous snakes found in the Indian subcontinent.
On April 25, 2020, a pink-skinned, black-eyed wall’s krait (Bungarus walli) was found in the Dhanushadham municipality in the province's Dhanusha District.
“The snake was kept inside a clay pot,” explained Ganesh Sah, a reptile rescuer and wildlife photographer who spoke with Global Voices by phone. He added that a villager initially assumed that he was not a rescuer but someone who wanted to profit from discovering the snake. “I had to convince the community members before they allowed me to release the snake into [its] natural habitat.”
A little over a month later, on June 3, Sah rescued another leucistic snake that had been discovered in Dhanushadham's Kishanpur region. This Bungarus niger species, commonly called the greater black krait, looked similar to the one found in Matiarba in April:
Leucism, a genetic condition that is often confused with albinism, is caused by either a complete or partial loss of pigmentation, resulting in white-coloured skin. Eye colour, however, is not affected.
Albinism, on the other hand, is caused by an absence of melanin, which is what gives skin and eyes their colour. The eyes of albino snakes appear pink because the blood vessels shine through their eyeballs.
In a telephone interview, Kamal Devkota, the lead author of the research paper, noted that either leucism or albinism in venomous snakes makes them more vulnerable: their appearance makes them easy to spot, so they often fall prey to predators, and their inability to camouflage presents them with difficulties in finding food. Moreover, they are unable to thermoregulate properly, which affects their movement and digestion.
The photographic guide Venomous Snakes of Nepal states that out of the 89 snake species recorded in the country, 17 — including six different species of kraits — are considered highly venomous and dangerous.
The Wall’s krait (Bungarus walli) variety has a head, body and tail that is typically shiny black, brownish-black or grey, with numerous narrow white or yellowish bands. It has been recorded in Nepal's southeast lowlands, the Gangetic floodplains of northern India, and Bangladesh's delta region.
The greater black krait (Bungarus niger) has a shiny black, brownish-black or dark chocolate head, body and tail with no bands or lines. It has been recorded in the lowlands and lower mountains of Nepal, Bhutan, India, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Kraits are usually active at night and their bites can prove fatal within as little as 24 hours. The World Health Organization estimates that 20,000 people are bitten by snakes each year in Nepal, and more than 1,000 of them die. Many studies suggest, however, that the figures may be higher.
Although less than 20 per cent of the snake species found in Nepal are highly venomous, people tend to be afraid of all snakes. Quite often, rat snakes — which are non-venomous — are mistaken for cobras, as are wolf snakes for kraits.
Such cases of mistaken identity usually result in the killing of these creatures, but awareness programmes and the establishment of snake information centres have helped change people’s perceptions as organisations and individuals alike have been rescuing snakes and educating people about them.
This article was previously published in Global Voices, an international and multilingual community of writers, translators, academics, and human rights activists.
News
3 min read
India’s inauguration of the link road to Mansarovar causes alarm in Nepal, but is a press statement enough?
Explainers
7 min read
Four Nepalis were recently arrested in possession of uranium. The Record explains what they were planning to do with it and how much it’s worth.
Perspectives
8 min read
Studies predict climate change will cause more dry spells and extreme seasonal rainfall in the future, increasing Nepal’s vulnerability to landslides.
Features
3 min read
Nepal’s migrant laborers are particularly vulnerable to the Covid19 outbreak in the absence of basic healthcare or job security.
News
5 min read
The Supreme Court’s decision is not just a win for the legal team but also for environmental activists who have been tirelessly campaigning against the construction of the airport for years.
Features
4 min read
Two-headed snakes are born due to many reasons
Photo Essays
3 min read
Aging gracefully has little to do with skincare and facelifts; aging with dignity is about honoring your age, your journey, and your being.
Perspectives
10 min read
Fossil fuel-enabled developed nations are now realizing that they are not immune to the impacts of climate change, but the worst effects will be--and are being--felt by poorer countries.